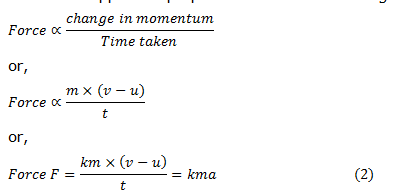Mathematically it describes the causes and effects of force and changes in motion of an object.
State newton s 2nd law of motion and derive an expression of force using the law.
The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force in the same direction as the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Before understanding the equation of newton s second law of motion which deals with force mass and acceleration of an object let s have a look upon the three laws of motion.
Derivation of conservation of momentum consider two colliding particles a and b whose masses are m1 and m2 with initial and final velocities as u 1 and v 1 of a and u 2 and v 2 of b.
If we consider the force to be a constant force then as a definition we state that impulse is the product of the force applied and.
The law of conservation of momentum is an important consequence of newton s third law of motion.
Newton s 2nd law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the.
The second law of motion is more quantitative and is used extensively to calculate what happens in situations involving a force.
Newton s second law states that the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object.
A force of 5 n produces an acceleration of 8 ms 2 on a mass m 1 and an acceleration of 24 ms 2 on a mass m z what acceleration would the same provide if both the masses are tied together.
Newton s second law of motion can be formally stated as follows.
The 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on the body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
The second law of motion describes what happens to the massive body when acted upon by an external force.
Derive the unit of force using the second law of motion.
It is also called the.
Defining newton s second law of motion.
In other words the state of motion of a body changes only on application of a net non zero force.
Consider a body of mass m moving with velocity v.
Second law of motion formula.
It means that the linear momentum will change faster when a bigger force is applied.
Newton s second law of motion states that the rate of change of momentum of an object or a system is proportional to the net force applied on that object or the system.
Newton s second law of motion.
Impulse momentum theorem derivation.
Derivation of newton s first law of motion from newton s second law of motion newton s first law states that a body stays at rest if it is at rest and moves with a constant velocity if already moving until a net force is applied to it.





.png)